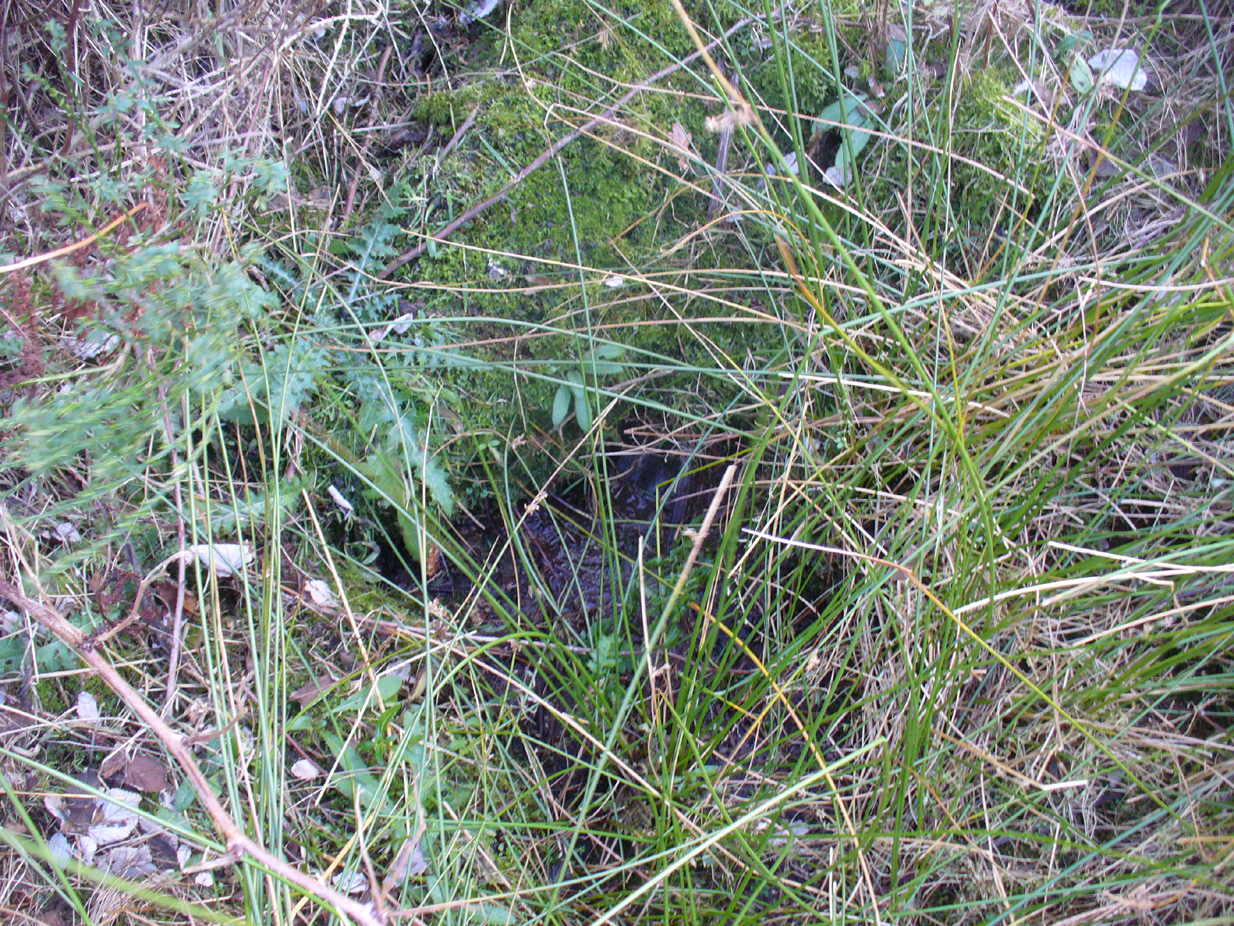
Healing Well (lost): OS Grid Reference – TQ 40 87
Also Known as:
- Wanstead Spring
Archaeology & History
The exact location of this site remains a mystery. Addison (1951) mentions it as being “close to the Blake Hall Road” where a drinking fountain was erected, but notes that this was not the original site of the spring. It was obviously a medicinal spring of some renown to the local people, before it was appropriated by the wealthy to turn it into a ‘spa well’. In doing so, it brought the attention of those curious lords and ladies, along with King James himself, adorning themselves in usual view as important people, and playing the part in social gatherings, as folks did at those spa wells. But the fad didn’t last long and the spa never really caught on. One account tells how it was a dangerous place for the rich and wealthy to visit! Locals can and do get pissed-off if you steal their basic water supplies!
The primary description of the site is that afforded by Christy & Thresh (1910) in their excellent survey of Essex waters. With no mention of the unimportant local people (!), they told how it was “first discovered” in the early 17th century:
“John Chamberlain, the news-letter writer, writing from London to Sir Dudley Carleton, on 23 August 1619, says:
“‘…We have great noise here of a new Spaa, or spring of that nature, found lately about Wansted; and much running there is to yt dayly, both by Lords and Ladies and other great companie, so that they have almost drawne yt drie alredy; and, yf yt should hold on, yt wold put downe the waters at Tunbridge; wch, for these three or foure yeares, have ben much frequented, specially this summer, by many great persons; insomuch that they wch have seene both say that yt [i.e., Tunbridge] is not inferior to the Spaa [in Belgium] for goode companie, numbers of people, and other appurtenances.”
“We have been quite unable to ascertain anything as to the part of Wanstead parish in which this spring was situated. In all probability, it was quite a small spring. One may infer as much from Chamberlain’s statement that, within a short time of its discovery, the company resorting to it had “almost drawn it dry.” If such was the case, the spring was, no doubt, soon deserted and ultimately forgotten.
“Mr. Walter Crouch, F.Z.S., of Wanstead, whose knowledge of the history of the parish is unequalled, writes us : —
“I have always had the idea that this Mineral Spring was not at the Park end of our parish, which abuts on Bush wood and Wanstead Flats, but in the vicinity of Snaresbrook and on the road which leads to Walthamstow; but it is possible that it was in the grounds of ‘ The Grove ‘ (now cut up and built over). The spring is not marked on Kip’s View (1710), nor on Rocque’s large Map (1735), nor on Rocque’s still larger map of a few years later.”
“Under the guidance of Mr. W. Ping, F.C.S., of Wanstead, Mr. Christy has visited two springs at Snaresbrook — namely, that known as the ‘Birch Well’, in the Forest, near the Eagle Pond, and a spring in the grounds of ‘The Hermitage’; but neither of these is credited locally with being a mineral spring and neither has any appearance of being such. Since then, Mr. Ping has written us as follows: “I have spoken with the oldest inhabitant of Wanstead, a Mr. Merryman, whose knowledge, both local and national, is remarkable and accurate. He tells me that the only Mineral Spring he ever heard of in Wanstead was in the grass bordering the roadside nearly opposite the house, in the Blake Hall Road, formerly occupied by Lord Mayor Figgis, and now by Sir John Bethell, M.P. This spring he remembers well. Its water was chalybeate and left considerable reddish deposit. People came and drank it to give them an appetite. They used to kneel down and drink it from their hands, and also took it away in bottles. Others used to bathe their ankles in it to make them strong. Mr. Merryman adds that, about 1870, drainage operations deprived the spring of its water. The fountain, which has since been put up near its site, supplies waterworks water only.” Mr. Ping adds that, recently when deeper drainage operations were in progress at the spot, water of a very markedly ferruginous character was encountered. This is no evidence that this spring was identical with that which came into prominence in 1619, but very likely it was.
“Mr. Dalton expresses the opinion that, if either surmise as to the position is correct, seeing that the comparison with the Tunbridge Wells chalybeate water was sound, the well in question probably yielded a ferruginous water from the Glacial (?) gravels of the Snaresbrook plateau at their contact with the pyritous London Clay.”
References:
- Addison, William, English Spas, Batsford: London 1951.
- Christy, Miller & Thresh, May, A History of the Mineral Waters and Medicinal Springs of the County of Essex, Essex Field Club: Stratford & London 1910.
- Hembry, Phyllis, The English Spa 1560-1815, Athlone Press: London 1990.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian