Cup-and-Ring Stone: OS Grid Reference – NZ 94 06?
Also Known as:
- Kendall Stone
Archaeology & History
In James Simpson’s precursory essay (1866) to his monumental Archaic Sculpturings (1867), he details the former existence of a decent piece of prehistoric rock art, lost to us until very recently by the intrusive diggings of one Thomas Kendall of Pickering. Simpson wrote:
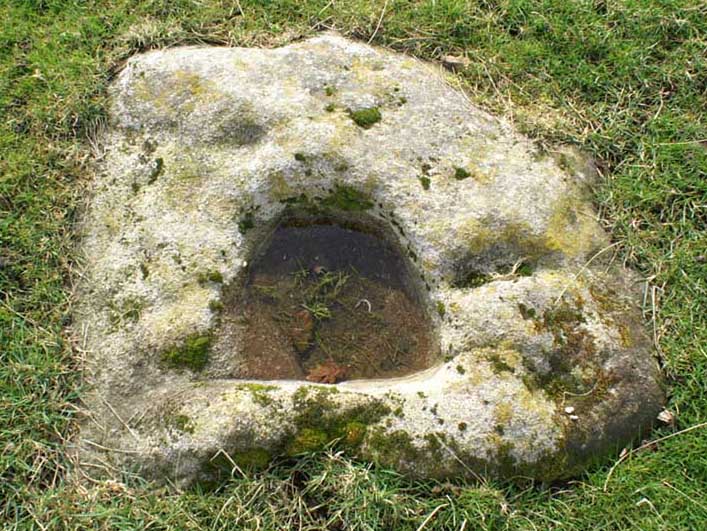
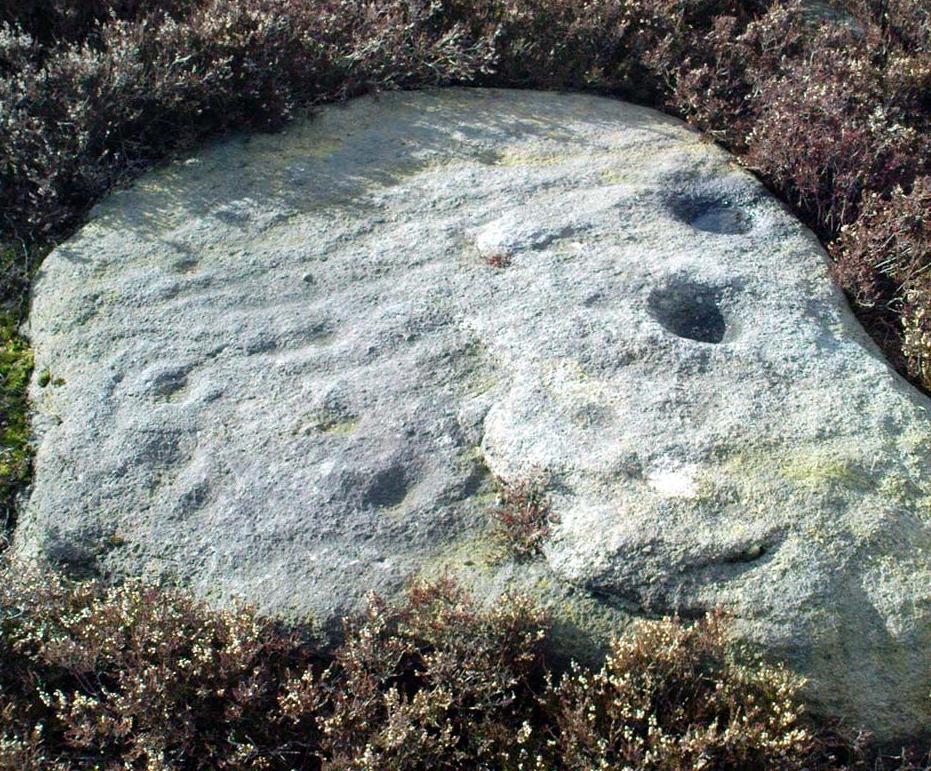
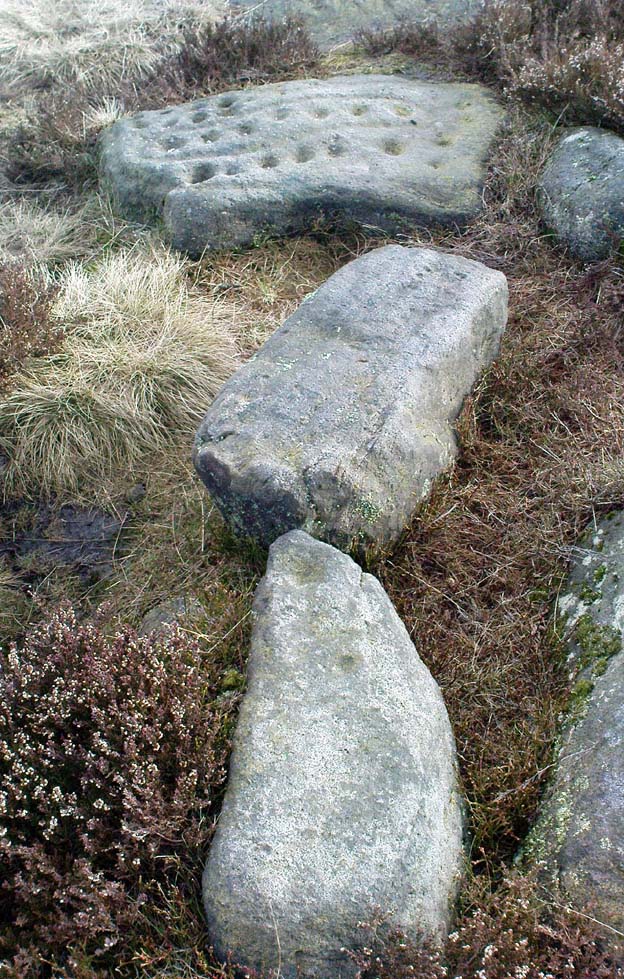
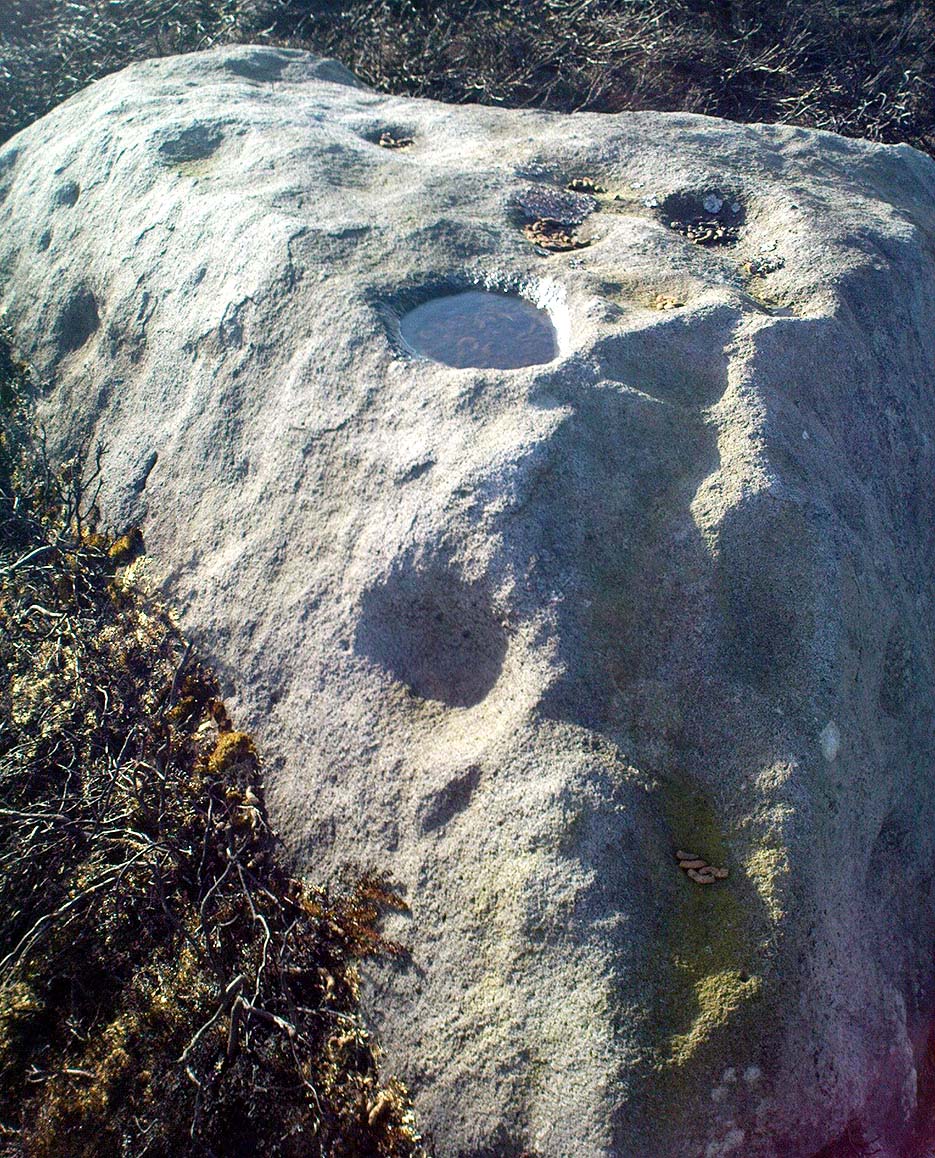
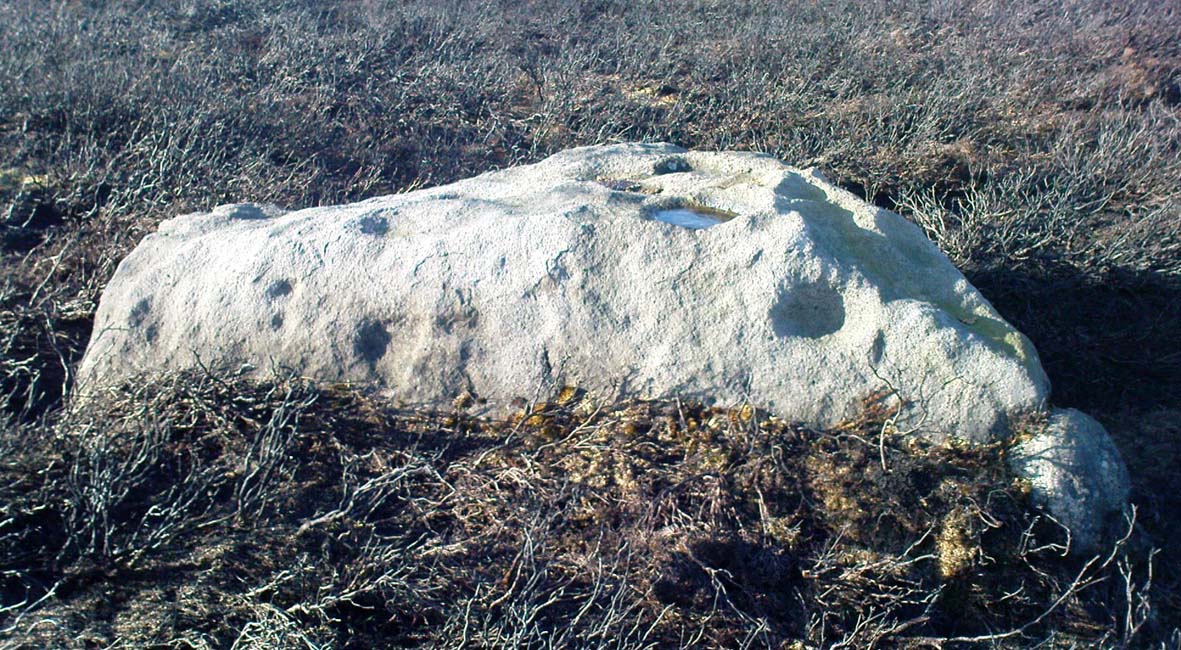
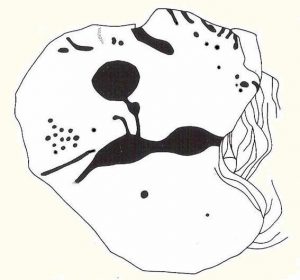
“A large mass of sandstone in the moor above Robin Hood’s Bay, near Whitby, had some sculpturings upon it, part of which were split off by Mr Kendall of Pickering, in whose garden I have seen the slab of carvings which he thus procured. Mr Kendall’s slab is about five feet long and two and a-half broad. Upon its surface are three or four isolated cups about an inch and a-half in breadth, and five or six others surrounded by ring-cuttings… Two or three of the ring-cuttings consist of single circles. One consists of a triple circle and straight radial groove. The ends of the circles, as they reach the traversing groove, turn round and unite together, as in the horse-shoe pattern… The two remaining circles, which are respectively five inches and eight inches in breadth, and consist of cups surrounded by two and by three circles, are conjoined together by a long gutter. The upper circle shows a single-and the lower a double horse-shoe pattern. In the uppermost or double circle the rounded ends of the rings are united and bestridden by a shallow right-angled line; and the ends of the lowest or triple circle are in part also conjoined by the gutter which runs from the double circle above, and by a cross straight line which runs off from it. The circles are more imperfectly finished than usual, and at some parts present almost an appearance of being punched out rather than cut out.”

In recent years, thanks to the cup-and-ring huntings of Chris Evans and Graeme Chappell, the carving has re-emerged from its lost position and, it would seem, is located in someone’s garden in Pickering. The carving is catalogued as Stone REM 1/P1 in Brown & Chappell’s (2005: 257) work on North Yorkshire rock art. Hopefully, in the months to come, we’ll have a decent photograph and description of its present condition. Fingers crossed!
References:
- Brown, P.M. & Chappell, Graeme, Prehistoric Rock Art in the North York Moors, Tempus: Stroud 2005.
- Simpson, J.Y., ‘On Ancient Sculpturings of Cups and Concentric Rings’, in PSAS volume 6, 1866.
- Simpson, James Y., Archaic Sculpturings of Cups, Circles, etc., upon Stones and Rocks in Scotland, England and Other Countries, Edmonston and Douglas: Oxford 1867.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian