‘Standing Stone’: OS Grid Reference – NO 15927 31609
Also Known as:
Going north-eastish from the city of Perth, take either the A93 or A94, turning west along the A93 a mile south of Guildtown, or east at Balbeggie on the A94, until you reach St. Martin’s hamlet and park up just below the church opposite the old cottages. Walk up the track below the cottages (not the one above them!) for ⅘-mile (1.35km) [past the ruined Cupar Stone Circle], and where the land has levelled out and in the huge flat field on your left, you’ll eventually reach a gate and see the odd-looking ‘rock’ about 250 yards away in the middle.
Archaeology & History
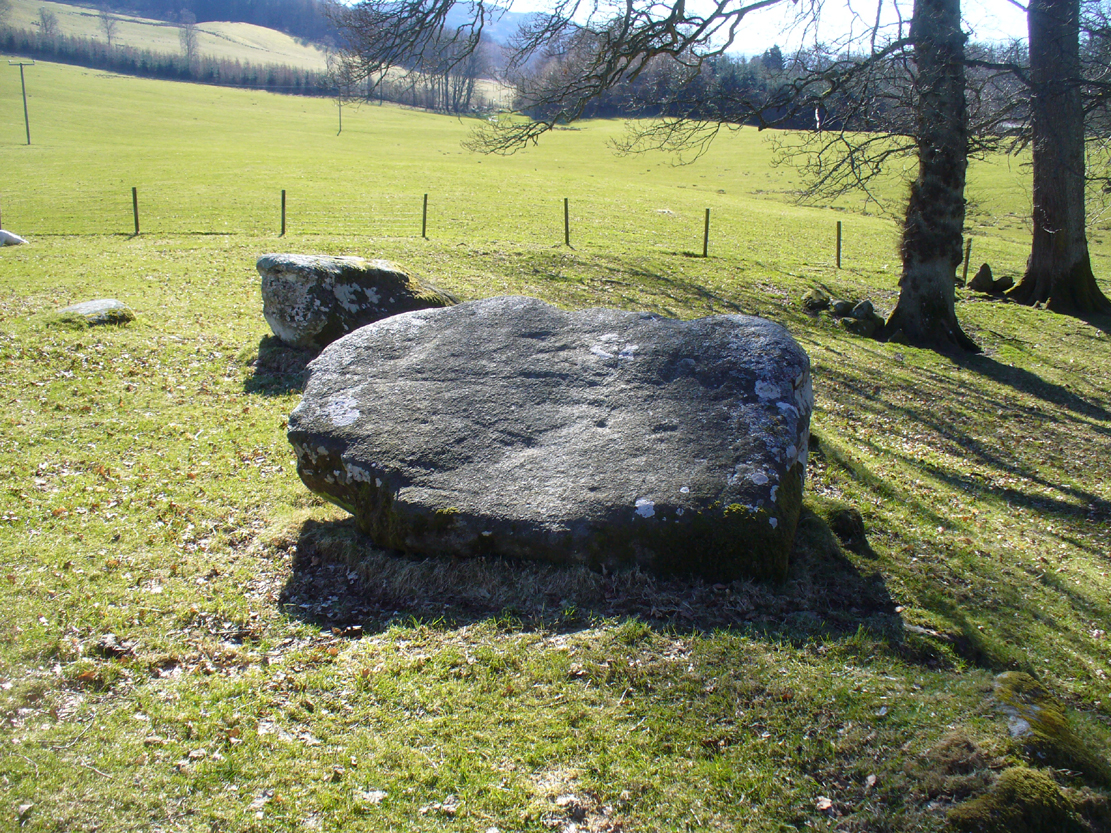
In a quiet and little-known parish that was once littered with about a dozen stone circles, there remains a most curious and fascinating stone which, in earlier days, was to be seen on the open moorlands at this spot. The area was then forested and then the agriculturalists came with their farming and destroyed the forests, leaving the old stone as it presently stands, isolated, above the hamlet of St. Martin’s to the south. Although it was described in the 19th century as being “four feet high”, it stands barely three feet tall, is very curiously-shaped—just like a morel mushroom from some angles—and in the middle of an extensive piece of flatland where the crops barely grow.
The stone was highlighted on the first OS-map of the parish in 1866, showing it in the woodland plantation of Eastmuir. It may have been some sort of northern outlier related to the now-destroyed stone circle of Cupar 400 yards south; and if this was the case, its position in the landscape relative to the circle would give the Witches Stone an airt (virtue ascribed to cardinal directions) in the cycle of the year that relates to darkness and death. (Perhaps oddly—perhaps not—the name of parish St. Martin’s relates to that dark period in the calendar, as St. Martin’s day in the old calendar was Samhain or Halloween: old New Year’s Day, when the spirits of the dead moved across both land and skies.)
It was erroneously described by the Canmore lads as being little more than “a glacial erratic”, but the stone here is quite earthfast; and their idea that “its peculiar shape has probably been caused by wind erosion”, is also somewhat dubious considering the shape of other monoliths and megalithic rings in the region. The stone has an appearance similar to some Bull Stones, where the animal was chained to rocks such as this and then baited by dogs, although I can find no such lore here. Indeed, the history and archaeology of the stone seems all but silent. Its folklore however, would have the Shakespearian romanciers amongst you flocking to the place…
The top of the stone has some very distinct and deep-cut lines running across it at angles, and has the appearance of being cut into at some time in the dim and distant past. By whom, and for what reason, we cannot say.
Folklore
William Richie (1845) told us that in the 11th Century when Scotland was having to deal with the english disease of stealing land and spreading its violence, King MacBeth—whose castle stood within this parish at Cairnbeddie (NO 1498 3082)—took that advice of two witches, and that
“they met him one night at a place still called ‘the Witch Stane’ (where a remarkable stone still stands), about a mile from his old residence, and warned him to beware, ‘Till Birnam forest come to Dunsinane.’”
The 1860 Name Book told us that,
“The Moor where the witches met, which is in St. Martins Parish is yet pointed out by the country people, and there is a stone still preserved, which is called the Witches Stone.”
References:
- Scott, Aleander, St. Martin’s and Cambusmichael, Perth 1911.
- Richie, William, “St. Martins and Cambusmichael,” in New Statistical Account of Scotland – volume 10: Perthshire, William Blackwood: Edinburgh 1845.
Acknowledgements: Huge thanks to Prof Paul Hornby for showing me this site. Cheers matey!
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian