Cairn (destroyed): OS Grid Reference – NZ 6950 1886
Archaeology & History
Another old site that has sadly succumbed to that bollox called ‘progress’! It’s in the North Yorkshire region some halfwits have taken to calling Cleveland — but which a lotta local folk still correctly call Yorkshire. But that aside…
In an article by local students William Hornsby and Richard Stanton written in 1917, we find that this was just one of at least seven hillocks presumed to be barrows here — but all the others had gone even in their day. When Crawford (1980) came to survey the site in the late 1970s, he told that,
“this large barrow is now only visible as a low swell in an arable field… (but) the profile of the barrow is retained in the hedgeline that bisects it from north to south, but the whole of its eastern half has been obliteratd by the Brotton-Kilton road.”

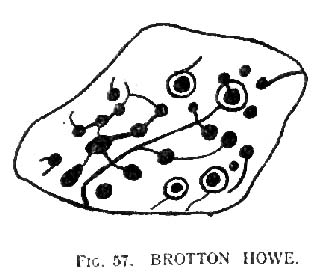
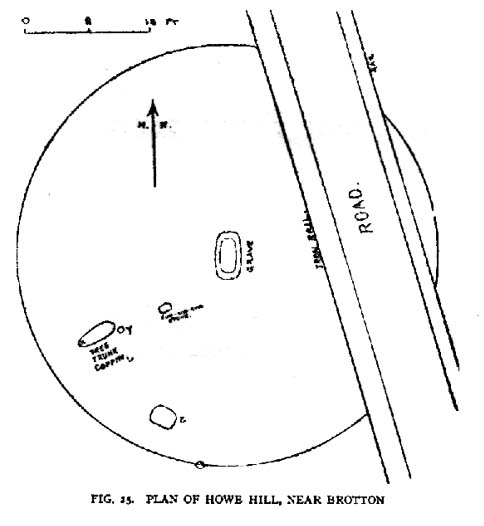
When Hornsby and Stanton checked the place out it measured 54 feet in diameter and had an extensive covering of small stones, like a large cairn, with a single grave at the centre, aligned north-south; and a tree-trunk coffin on the southwestern side. Of the stones which filled the central grave, eight of them were found to have cup-markings on them; whilst 16 stones covering the tree-trunk grave also possessed cup-markings. Roughly equidistant between the two burials was another stone found to be resting face-down on the original ground-level, and covered with 20 cups and 5 cup-and-rings! Awesome stuff!
G.M. Crawford’s (1980) description of the site was as follows:
“Howe Hill was excavated by Hornsby and Stanton in 1914; they discovered that the mound was made up with a clay floor, overlain by ‘a cairn 30 feet long and 3 feet high’ of diorite cobbles, capped by a layer of earth. Cut into the clay floor were two graves: the first was oriented north-south and measured 2m long by 0.9m wide at the old land surface and was 0.7m deep. The grave was filled with ‘medium sized stones’ with a ‘thin dark layer,’ thought to be an inhumation burial, on the floor; 8 of the stones bore cup-marks. The second grave, oriented northeast-southwest, was 2.5m long by 0.9m wide at the old ground surface, reducing to 1.8m long by 0.5m wide at its bottom, 1.3m below. This grave, which was filled with stones, also contained a tree-trunk coffin or oak, measuring 1.5m long… At the head (northeast) were found the unburnt skull fragments of a man laid on its right side. Unaccompanied cremations had been placed at both ends of the coffin. 16 cup-marked stones were among the infill of the grave.”
This was obviously a site of considerable importance and it’s a huge pity (if not a disgrace) that today no trace of the site remains.
References:
- Cowling, Eric T., Rombald’s Way, William Walker: Otley 1946.
- Crawford, G.M., Bronze Age Burial Mounds in Cleveland, Cleveland County Council 1990.
- Elgee, Frank, Early Man in North-east Yorkshire, John Bellows: Gloucester 1930.
- Hornsby, William & Stanton, Richard, “British Barrows near Brotton,” in Yorkshire Archaeology Journal, 24, 1917.
- Smith, A.H., The Place-Names of the North Riding of Yorkshire, Cambridge University Press 1928.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian