‘Carved Stone’: OS Grid Reference – SD 93 72
Archaeology & History
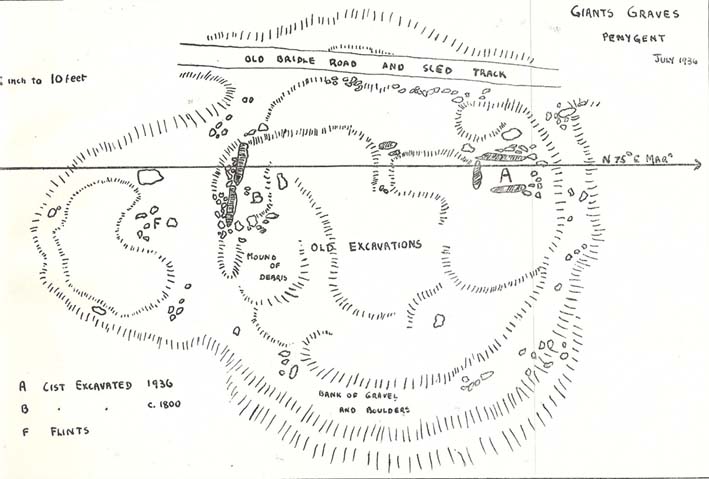
This is a frustrating site entry. Not only do we not know where it is, this carving is not listed in any of the modern books on British petroglyphs, yet it was described and referenced by the famous archaeologist Jacquetta Hawkes following its discovery more than 80 years ago. After a brief mention of the carving in Frank Elgee’s (1933) Archaeology of Yorkshire, an article describing the carving was penned in the journal Man, from which I draw the only information available. It appears to have been found in the early 1930s (no date or discoverer is cited), but has a couple of peculiarities which may bring the authenticity of the stone into question. Mrs Hawkes (1934) told that the carved stone was,
“found in the bed of a moorland beck in the village of Arncliffe, Littondale, West Riding of Yorkshire. It is of buff-coloured limestone measuring 21 inches x 12 inches x 6 inches in thickness; the decorated surface is almost flat. The curvilinear pattern is executed in regular incisions about 4mm wide and 3mm deep; portions of it have been obliterated by water actions and, as is illustrated in the illustration, at one end the surface has broken away altogether. The whole stone has been much battered and may well be only a fragment of a much larger one. The state of preservation suggested that it had been in the stream for a considerable period; it is therefore probable that it was washed down from the open moorland above Arncliffe. In the original (carving), the design is more coherent than it here appears owing to the fact that in the water-worn portions faint lines are visible to the eye which cannot be shown on a tracing.
“Mr W.J. Hemp, who has kindly examined the Arncliffe tracing, identifies the style of the design with the ‘entrail’ pattern of the well-known Pattern Stone from the chambered cairn of Bryn Celli Ddu in Anglesey…
“The technique of the Arncliffe tracing is comparable with the simple incisions which form the oldest of the four techniques recognizable in the Irish megalithic tumuli, where its early date is indicated by the fact that some examples are demonstrably older than the construction of the tumuli in which they occur…
“Mr Frank Elgee, who has also been good enough to comment on the Arncliffe tracing, cannot suggest immediate comparisons from this neighbouring group (around Ilkley, PB), but such evidence as there is he considers to be against assigning a date earlier than the MIddle Bronze Age.”
The late great Eric Cowling also mentioned the stone in his prehistoric survey of the mid-Pennines, but added no further details of his own and seems to have just copied what we have just read.
The fact that the ‘carving’ was found in a stream-bed may mean that the markings on the stone were due to natural erosion; and the fact that the rock was limestone may give added weight to this idea. However, the fact that Mrs Hawkes, Frank Elgee and W.J. Hemp thought the carving to be authentic cannot be overlooked. The area is also rich in prehistoric remains (see Douky Bottom, Dewbottoms, Yockenthwaite, Blue Scar, etc) The design itself is an odd one and has none of the traditional hallmarks consistent with neolithic and Bronze Age cup-and-ring stones, but seems more reminiscent of much earlier mesolithic and palaeolithic images of carved animals and dancing human figures.
If anyone knows more about this site, particularly its whereabouts (perhaps in private possession or hiding in some museum box, where increasing numbers of cup-and-rings are wrongfully kept), or whether the ‘carving’ has been disregarded as little more than natural weathering, it would be good to know for certain.
References:
- Cowling, E.T., Rombald’s Way: A Prehistory of Mid-Wharfedale, William Walker: Otley 1946.
- Elgee, Frank & Harriet, The Archaeology of Yorkshire, Methuen: London 1933.
- Hawkes, Jacquetta, “A Prehistoric Carved Stone in Littondale,” in Man, volume 34, 1934.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian