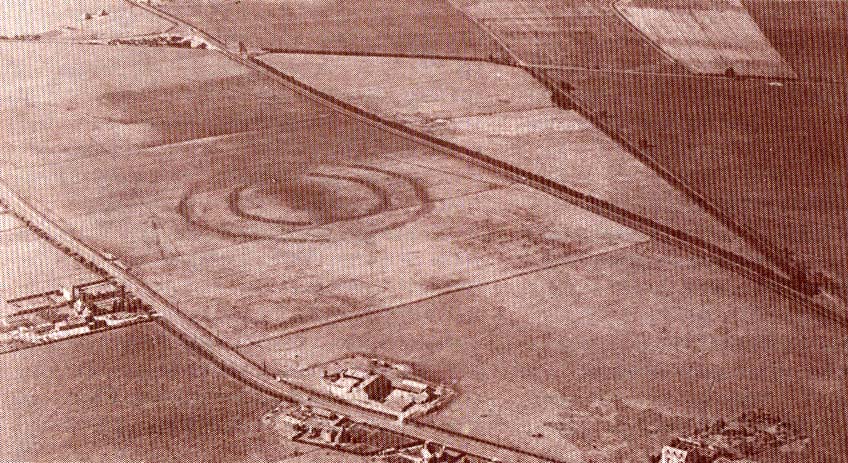
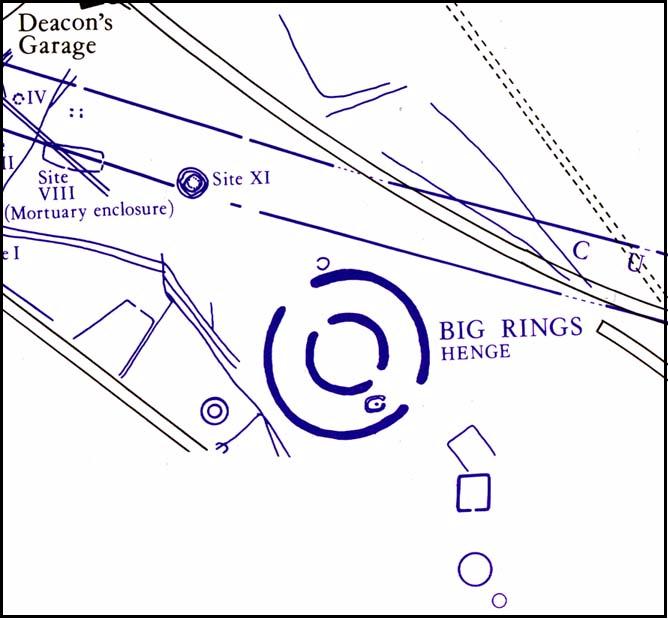
Timber Circle (destroyed): OS Grid Reference – SU 5775 9513
Also Known as:
- Dorchester 3
- NMR NUMBER: SU 59 NE 53
- Site no. 371.21.1
Archaeology & History
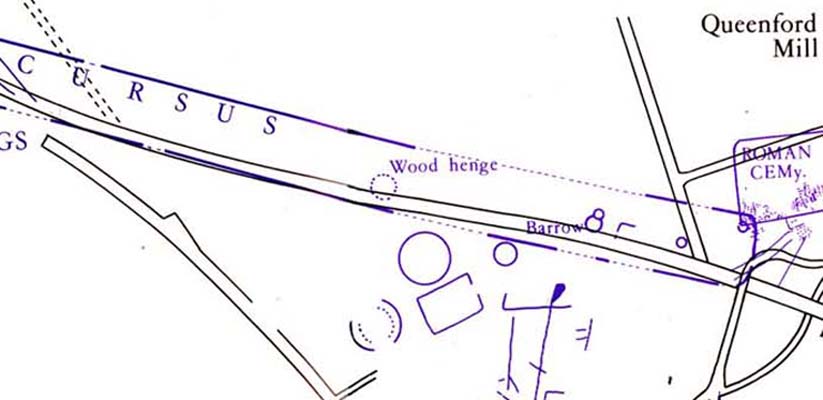
Although ascribed as a wooden ‘henge’ by archaeologist Jean Cook, the site is more accurately a simple timber circle. Cook (1985) described this little-known “Wood Henge” monument, as she called it, sat inside the lower southeastern end of the impressive Dorchester Cursus monument. The site was obviously of some ritual importance, for a variety of reasons. It was excavated in 1981 and,
“it consisted of a ring of large pits enclosing an area some 18m in diameter. The site was situated along the central axis of the (Dorchester) cursus, presumably influenced by the alignment. The pits, which varied in size, had each contained a wooden post, in three instances consisting of an entire trunk of an oak tree. All the posts were burnt in situ, presumably during some form of destruction ceremony.”
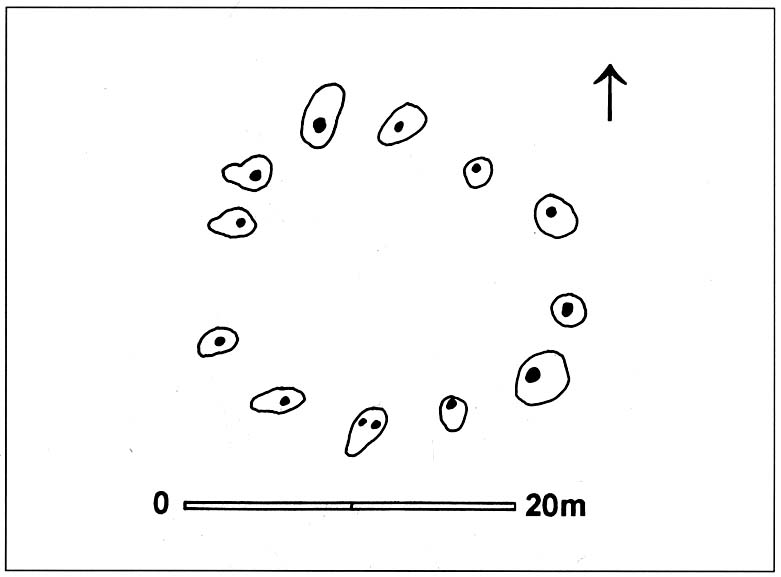
When Alex Gibson came here a few years afterwards to re-examine the site, his work and that of Richard Bradley (1988) also found the place to have been an elliptical ‘ring’ of once-upright timber posts. Although Gibson (1998) later gave a confused version of where the site actually was (wrong grid-refs), his brief description gave us an outline of what was once here:
“An oval of 12 postholes containing the carbonized remains of 13 posts which had been burnt prior to the placing of cremations in the upper fills of the postholes. The SW posthole contained the remains of two posts in the same socket. There is a possible entranceway, marked by a wider gap between posts, in the NW.”
But this last line appears to be pure speculation. I’ve not read the longer archaeological accounts of this ‘wood henge’ and adjacent sites (Bradley & Chambers, 1988; Gibson 1992), which should give greater details about the site as a whole. The Pastscape site gives the following information:
“A pit circle comprising a sub-circular arrangement of 12 pits was excavated in the early 1980s in advance of work on the Dorchester by-pass. The site lay within the Dorchester Cursus (SU 59 NE 5), circa 400 metres northwest of its southeastern terminal. The long axis of the pit circle was the same as that of the cursus. Each of the pits had held a timber upright, and some if not all had been burnt in situ. An air photograph of the site had suggested the presence of a central pit but this feature proved to be a natural pocket of sand. Six deposits of cremated bone came from various post pipes. Other finds included a handful of potsherds, one possibly of Early Bronze Age date, some animal bone fragments, and a few flints. Radiocarbon dates from cremated bone and charcoal centred on the mid 3rd millennium BC, with one slightly later.”
References:
- Bradley, R. & Chambers, R., “A New Study of the Cursus Complex at Dorchester-on-Thames, in Oxford Journal of Archaeology, volume 7, 1988.
- Cook, Jean, “The Earliest Evidence,” in Dorchester through the Ages, Oxford University 1985.
- Cook, Jean & Rowley, Trevor (eds.), Dorchester through the Ages, Oxford University 1985.
- Gibson, Alex, “Possible Timber Circles at Dorchester-on-Thames,” in Oxford Journal of Archaeology, volume 11, 1992.
- Gibson, Alex, Stonehenge and Timber Circles, Tempus: Stroud 1998.
- Pennick, Nigel & Devereux, Paul, Lines on the Landscape, Hale: London 1989.
© Paul Bennett, The Northern Antiquarian